Herpes simplex virus
| Herpes simplex virus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
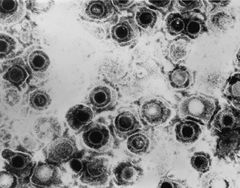
| TEM micrograph of a herpes simplex virus. | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group I (dsDNA) |
| Family: | Herpesviridae |
| Subfamily: | Alphaherpesvirinae |
| Genus: | Simplexvirus |
| Species | |
|
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HWJ-1) |
|
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known as Human herpes virus 1 and 2 (HHV-1 and -2), are two members of the herpes virus family, Herpesviridae, that infect humans.[1] Both HSV-1 and -2 are ubiquitous and contagious. They can be spread when an infected person is producing and shedding the virus.
Symptoms of herpes simplex virus infection include watery blisters in the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth, lips or genitals.[1] Lesions heal with a scab characteristic of herpetic disease. Sometimes, the viruses cause very mild or atypical symptoms during outbreaks. However, as neurotropic and neuroinvasive viruses, HSV-1 and -2 persist in the body by becoming latent and hiding from the immune system in the cell bodies of nerves. After the initial or primary infection, some infected people experience sporadic episodes of viral reactivation or outbreaks. In an outbreak, the virus in a nerve cell becomes active and is transported via the nerve's axon to the skin, where virus replication and shedding occur and cause new sores.[2]
Contents |
Transmission
HSV-1 and -2 are transmitted from contact with an infectious area of the skin during reactivations of the virus. The herpes viruses cannot be transmitted during latency. Transmission is likely to occur during symptomatic reactivation of the virus that causes visible and typical skin sores. Asymptomatic reactivation means that the virus causes atypical, subtle or hard to notice symptoms that are not identified as an active herpes infection. Atypical symptoms are often attributed to other causes such as a yeast infection.[3] [4] HSV-1 is usually acquired orally during childhood, but may also be sexually transmitted. HSV-2 is primarily a sexually transmitted infection but rates of HSV-1 genital infections are increasing.[3]
Both viruses may also be transmitted vertically during childbirth, although the real risk is very low. [5] The risk of infection is minimal if the mother has no symptoms or exposed blisters during delivery. The risk is considerable when the mother gets the virus for the first time during late pregnancy. [6]
Symptoms resulting from primary infection with HSV are usually much more severe than subsequent outbreaks, as the body has not had a chance to produce antibodies. This first outbreak of oral herpes (cold sores) carries a low (≈1%) risk of developing aseptic meningitis.[1]
Microbiology
Viral structure
Animal herpes viruses all share some common properties. The structure of herpes viruses consists of a relatively large double-stranded, linear DNA genome encased within an icosahedral protein cage called the capsid, which is wrapped in a lipid bilayer called the envelope. The envelope is joined to the capsid by means of a tegument. This complete particle is known as the virion.[7] HSV-1 and HSV-2 each contain at least 74 genes (or open-reading frames, ORFs) within their genomes,[8] although speculation over gene crowding allows as many as 84 unique protein coding genes by 94 putative ORFs.[9] These genes encode a variety of proteins involved in forming the capsid, tegument and envelope of the virus, as well as controlling the replication and infectivity of the virus. These genes and their functions are summarized in the table below.
The genomes of HSV-1 and HSV-2 are complex and contain two unique regions called the long unique region (UL) and the short unique region (US). Of the 74 known ORFs, UL contains 56 viral genes, whereas US contains only 12.[8] Transcription of HSV genes is catalyzed by RNA polymerase II of the infected host.[8] Immediate early genes, which encode proteins that regulate the expression of early and late viral genes, are the first to be expressed following infection. Early gene expression follows, to allow the synthesis of enzymes involved in DNA replication and the production of certain envelope glycoproteins. Expression of late genes occurs last; this group of genes predominantly encode proteins that form the virion particle.[8]
Five proteins from (UL) form the viral capsid; UL6, UL18, UL35, UL38 and the major capsid protein UL19.[7]
| The open reading frames (ORFs) of HSV-1[8][10] | |||||
| Gene | Protein | Function/description | Gene | Protein | Function/description |
| UL1 | Glycoprotein L [1] | Surface and membrane | UL38 | UL38; VP19C [2] | Capsid assembly and DNA maturation |
| UL2 | UL2 [3] | Uracil-DNA glycosylase | UL39 | UL39 [4] | Ribonucleotide reductase (Large subunit) |
| UL3 | UL3 [5] | unknown | UL40 | UL40 [6] | Ribonucleotide reductase (Small subunit) |
| UL4 | UL4 [7] | unknown | UL41 | UL41; VHS [8] | Tegument protein; Virion host shutoff[11] |
| UL5 | UL5 [9] | DNA replication | UL42 | UL42 [10] | DNA polymerase processivity factor |
| UL6 | UL6 [11] | Processing and packaging DNA | UL43 | UL43 [12] | Membrane protein |
| UL7 | UL7 [13] | Virion maturation | UL44 | Glycoprotein C [14] | Surface and membrane |
| UL8 | UL8 [15] | DNA helicase/primase complex-associated protein | UL45 | UL45 [16] | Membrane protein; C-type lectin[12] |
| UL9 | UL9 [17] | Replication origin-binding protein | UL46 | VP11/12 [18] | Tegument proteins |
| UL10 | Glycoprotein M [19] | Surface and membrane | UL47 | UL47; VP13/14 [20] | Tegument protein |
| UL11 | UL11 [21] | virion exit and secondary envelopment | UL48 | VP16 (Alpha-TIF) [22] | Virion maturation; activate IEGs by interacting with the cellular transcription factors Oct-1 and HCF. Binds to the sequence 5'TAATGARAT3'. |
| UL12 | UL12 [23] | Alkaline exonuclease | UL49 | UL49A [24] | Envelope protein |
| UL13 | UL13 [25] | Serine-threonine protein kinase | UL50 | UL50 [26] | dUTP diphosphatase |
| UL14 | UL14 [27] | Tegument protein | UL51 | UL51 [28] | Tegument protein |
| UL15 | Terminase [29] | Processing and packaging of DNA | UL52 | UL52 [30] | DNA helicase/primase complex protein |
| UL16 | UL16 [31] | Tegument protein | UL53 | Glycoprotein K [32] | Surface and membrane |
| UL17 | UL17 [33] | Processing and packaging DNA | UL54 | IE63; ICP27 [34] | Transcriptional regulation |
| UL18 | VP23 [35] | Capsid protein | UL55 | UL55 [36] | Unknown |
| UL19 | VP5 [37] | Major capsid protein | UL56 | UL56 [38] | Unknown |
| UL20 | UL20 [39] | Membrane protein | US1 | ICP22; IE68 [40] | Viral replication |
| UL21 | UL21 [41] | Tegument protein[13] | US2 | US2 [42] | Unknown |
| UL22 | Glycoprotein H [43] | Surface and membrane | US3 | US3 [44] | Serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| UL23 | Thymidine kinase [45] | Peripheral to DNA replication | US4 | Glycoprotein G [46] | Surface and membrane |
| UL24 | UL24 [47] | unknown | US5 | Glycoprotein J [48] | Surface and membrane |
| UL25 | UL25 [49] | Processing and packaging DNA | US6 | Glycoprotein D [50] | Surface and membrane |
| UL26 | P40; VP24; VP22A [51] | Capsid protein | US7 | Glycoprotein I [52] | Surface and membrane |
| UL27 | Glycoprotein B [53] | Surface and membrane | US8 | Glycoprotein E [54] | Surface and membrane |
| UL28 | ICP18.5 [55] | Processing and packaging DNA | US9 | US9 [56] | Tegument protein |
| UL29 | UL29; ICP8 [57] | Major DNA-binding protein | US10 | US10 [58] | Capsid/Tegument protein |
| UL30 | DNA polymerase [59] | DNA replication | US11 | US11; Vmw21 [60] | Binds DNA and RNA |
| UL31 | UL31 [61] | Nuclear matrix protein | US12 | ICP47; IE12 [62] | Inhibits MHC class I pathway by preventing binding of antigen to TAP |
| UL32 | UL32 [63] | Envelope glycoprotein | RS1 | ICP4; IE175 [64] | Activates gene transcription |
| UL33 | UL33 [65] | Processing and packaging DNA | ICP0 | ICP0; IE110; α0 [66] | E3 ubiquitin ligase that activates viral gene transcription and counteracts the interferon response |
| UL34 | UL34 [67] | Inner nuclear membrane protein | LRP1 | LRP1 [68] | Latency-related protein |
| UL35 | VP26 [69] | Capsid protein | LRP2 | LRP2 [70] | Latency-related protein |
| UL36 | UL36 [71] | Large tegument protein | RL1 | RL1; ICP34.5 [72] | Neurovirulence factor. Antagonizes PKR by de-phosphorylating eIF4a. |
| UL37 | UL37 [73] | Capsid assembly | LAT | none [74] | Latency-associated transcript |
Cellular entry
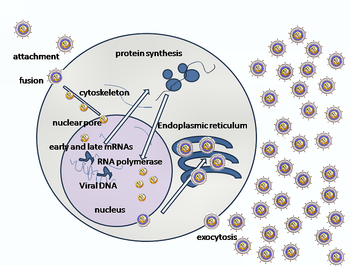
Entry of HSV into the host cell involves interactions of several glycoproteins on the surface of the enveloped virus, with receptors on the surface of the host cell. The envelope covering the virus particle, when bound to specific receptors on the cell surface, will fuse with the host cell membrane and create an opening, or pore, through which the virus enters the host cell.
The sequential stages of HSV entry are analogous to those of other viruses. At first, complementary receptors on the virus and the cell surface bring the viral and cell membranes into proximity. In an intermediate state, the two membranes begin to merge, forming a hemifusion state. Finally, a stable entry pore is formed through which the viral envelope contents are introduced to the host cell.[14] In the case of a herpes virus, initial interactions occur when a viral envelope glycoprotein called glycoprotein C (gC) binds to a cell surface particle called heparan sulfate. A second glycoprotein, glycoprotein D (gD), binds specifically to at least one of three known entry receptors. These include herpesvirus entry mediator(HVEM), nectin-1 and 3-O sulfated heparan sulfate. The receptor provides a strong, fixed attachment to the host cell. These interactions bring the membrane surfaces into mutual proximity and allow for other glycoproteins embedded in the viral envelope to interact with other cell surface molecules. Once bound to the HVEM, gD changes its conformation and interacts with viral glycoproteins H (gH) and L (gL), which form a complex. The interaction of these membrane proteins results in the hemifusion state. Afterward, gB interaction with the gH/gL complex creates an entry pore for the viral capsid.[14] Glycoprotein B interacts with glycosaminoglycans on the surface of the host cell.
Genetic inoculation
After the viral capsid enters the cellular cytoplasm, it is transported to the cell nucleus. Once attached to the nucleus at a nuclear entry pore, the capsid ejects its DNA contents via the capsid portal. The capsid portal is formed by twelve copies of portal protein, UL6, arranged as a ring; the proteins contain a leucine zipper sequence of amino acids which allow them to adhere to each other.[15] Each icosahedral capsid contains a single portal, located in one vertex.[16][17] The DNA exits the capsid in a single linear segment.[18]
Immune evasion
HSV evades the immune system through interference with MHC class I presentation of antigen on the cell surface. This is achieved through blockade of the TAP transporter induced by the secretion of ICP-47[19] by HSV. TAP maintains the integrity of the MHC class I molecule before it is transported via the golgi apparatus for recognition by CD8+ CTLs on the cell surface. ICP-47 disrupts this integrity, preventing the capture of cytosolic proteins for CTL recognition and thus evades CTL destruction.
Replication

Following infection of a cell, herpes virus proteins, called immediate-early, early, and late, are produced. Research using flow cytometry on another member of the herpes virus family, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, indicates the possibility of an additional lytic stage, delayed-late.[20] These stages of lytic infection, particularly late lytic, are distinct from the latency stage. In the case of HSV-1, no protein products are detected during latency, whereas they are detected during the lytic cycle.
The early proteins transcribed are used in the regulation of genetic replication of the virus. On entering the cell, an α-TIF protein joins the viral particle and aids in immediate-early transcription. The virion host shutoff protein (VHS or UL41) is very important to viral replication.[11] This enzyme shuts off protein synthesis in the host, degrades host mRNA, helps in viral replication, and regulates gene expression of viral proteins. The viral genome immediately travels to the nucleus but the VHS protein remains in the cytoplasm.[21][22]
The late proteins are used in to form the capsid and the receptors on the surface of the virus. Packaging of the viral particles — including the genome, core and the capsid - occurs in the nucleus of the cell. Here, concatemers of the viral genome are separated by cleavage and are placed into pre-formed capsids. HSV-1 undergoes a process of primary and secondary envelopment. The primary envelope is acquired by budding into the inner nuclear membrane of the cell. This then fuses with the outer nuclear membrane releasing a naked capsid into the cytoplasm. The virus acquires its final envelope by budding into cytoplasmic vesicles.[23]
Latent infection
HSVs may persist in a quiescent but persistent form known as latent infection, notably in neural ganglia.[1] HSV-1 tends to reside in the trigeminal ganglia, while HSV-2 tends to reside in the sacral ganglia, but note that these are tendencies only, not fixed behavior. During such latent infection of a cell, HSVs express Latency Associated Transcript (LAT) RNA. LAT is known to regulate the host cell genome and interferes with natural cell death mechanisms. By maintaining the host cells, LAT expression preserves a reservoir of the virus, which allows subsequent, usually symptomatic, periodic recurrences or "outbreaks" characteristic of non-latency. Whether or not recurrences are noticeable (symptomatic) or not, viral shedding occurs to produce further infections (usually in a new host, if any). A protein found in neurons may bind to herpes virus DNA and regulate latency. Herpes virus DNA contains a gene for a protein called ICP4, which is an important transactivator of genes associated with lytic infection in HSV-1.[24] Elements surrounding the gene for ICP4 bind a protein known as the human neuronal protein Neuronal Restrictive Silencing Factor (NRSF) or human Repressor Element Silencing Transcription Factor (REST). When bound to the viral DNA elements, histone deacytalization occurs atop the ICP4 gene sequence to prevent initiation of transcription from this gene, thereby preventing transcription of other viral genes involved in the lytic cycle.[24][25] Another HSV protein reverses the inhibition of ICP4 protein synthesis. ICP0 dissociates NRSF from the ICP4 gene and thus prevents silencing of the viral DNA.[26]
The virus can be reactivated by illnesses such as colds and influenza, eczema, emotional and physical stress, exposure to bright sunlight, gastric upset, fatigue or injury, and by menstruation.
Treatment and vaccine development
- For more details on treatment of herpes simplex virus, see Herpes simplex.
Herpes viruses establish lifelong infections and the virus cannot currently be eradicated from the body. Treatment usually involves general-purpose antiviral drugs that interfere with viral replication, reducing the physical severity of outbreak-associated lesions and lowering the chance of transmission to others. Studies of vulnerable patient populations have indicated that daily use of antivirals such as acyclovir and valacyclovir can reduce reactivation rates.[4]
In vitro research has indicated that Aloe Vera may be effective against genital herpes.[27]
Research into a vaccine is ongoing. Efforts to develop an effective vaccine have so far been hampered by the many adaptations of HSVs to their human hosts during an evolutionarily ancient relationship.[4] One of the most notable vaccines in development at this time is ImmunoVEXHSV2 from Biovex.[28]
Connection with Alzheimer's disease
A possible link between HSV-1 (ie, the virus that causes cold sores or oral herpes) and Alzheimer’s disease was reported in 1979.[29] In the presence of a certain gene variation (APOE-epsilon4 allele carriers), HSV-1 appears to be particularly damaging to the nervous system and increases one’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. The virus interacts with the components and receptors of lipoproteins, which may lead to the development of Alzheimer's disease.[30] This research identifies HSVs as the pathogen most clearly linked to the establishment of Alzheimer’s.[31] Without the presence of the gene allele, HSV-1 does not appear to cause any neurological damage or increase the risk of Alzheimer’s.[32]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 555–62. ISBN 0838585299.
- ↑ "Herpes simplex". DermNet NZ — New Zealand Dermatological Society. 2006-09-16. http://www.dermnetnz.org/viral/herpes-simplex.html. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Gupta R, Warren T, Wald A (2007). "Genital herpes". Lancet 370 (9605): 2127–37. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61908-4. PMID 18156035.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Koelle DM, Corey L (2008). "Herpes simplex: insights on pathogenesis and possible vaccines". Annual Review of Medicine 59: 381–95. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.59.061606.095540. PMID 18186706.
- ↑ Corey L, Wald A (2009). "Maternal and Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus Infections". New England Journal of Medicine 361 (14): 1376–85. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0807633. PMID 19797284.
- ↑ Kimberlin DW (2007). "Herpes simplex virus infections of the newborn". Semin. Perinatol. 31 (1): 19–25. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2007.01.003. PMID 17317423.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Mettenleiter TC, Klupp BG, Granzow H (2006). "Herpesvirus assembly: a tale of two membranes". Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9 (4): 423–9. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2006.06.013. PMID 16814597.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 McGeoch DJ, Rixon FJ, Davison AJ (2006). "Topics in herpesvirus genomics and evolution". Virus Res. 117 (1): 90–104. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2006.01.002. PMID 16490275.
- ↑ Rajcáni J, Andrea V, Ingeborg R (2004). "Peculiarities of herpes simplex virus (HSV) transcription: an overview". Virus Genes 28 (3): 293–310. doi:10.1023/B:VIRU.0000025777.62826.92. PMID 15266111.
- ↑ Search in UniProt Knowledgebase (Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL) for: HHV1
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Matis J, Kúdelová M (2001). "Early shutoff of host protein synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex viruses". Acta Virol. 45 (5-6): 269–77. PMID 12083325.
- ↑ Wyrwicz LS, Ginalski K, Rychlewski L (2007). "HSV-1 UL45 encodes a carbohydrate binding C-type lectin protein". Cell Cycle 7 (2): 269–71. PMID 18256535.
- ↑ Vittone V, Diefenbach E, Triffett D, Douglas MW, Cunningham AL, Diefenbach RJ (2005). "Determination of interactions between tegument proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1". J. Virol. 79 (15): 9566–71. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.15.9566-9571.2005. PMID 16014918.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Subramanian RP, Geraghty RJ (2007). "Herpes simplex virus type 1 mediates fusion through a hemifusion intermediate by sequential activity of glycoproteins D, H, L, and B". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (8): 2903–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608374104. PMID 17299053.
- ↑ Cardone G, Winkler DC, Trus BL, Cheng N, Heuser JE, Newcomb WW, Brown JC, Steven AC (May 2007). "Visualization of the herpes simplex virus portal in situ by cryo-electron tomography". Virology 361 (2): 426–34. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.047. PMID 17188319.
- ↑ Trus BL, Cheng N, Newcomb WW, Homa FL, Brown JC, Steven AC (November 2004). "Structure and polymorphism of the UL6 portal protein of herpes simplex virus type 1". Journal of Virology 78 (22): 12668–71. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.22.12668-12671.2004. PMID 15507654.
- ↑ Nellissery JK, Szczepaniak R, Lamberti C, Weller SK (2007-06-20). "A putative leucine zipper within the HSV-1 UL6 protein is required for portal ring formation". Journal Virology 81 (17): 8868–77. doi:10.1128/JVI.00739-07. PMID 17581990.
- ↑ Newcomb WW, Booy FP, Brown JC (2007). "Uncoating the herpes simplex virus genome". J. Mol. Biol. 370 (4): 633–42. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.023. PMID 17540405.
- ↑ Abbas et al (2009) Cellular and Molecular Immunology, Elsevier Inc.
- ↑ Adang LA, Parsons CH, Kedes DH (2006). "Asynchronous progression through the lytic cascade and variations in intracellular viral loads revealed by high-throughput single-cell analysis of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection". J. Virol. 80 (20): 10073–82. doi:10.1128/JVI.01156-06. PMID 17005685.
- ↑ Taddeo B, Roizman B (2006). "The virion host shutoff protein (UL41) of herpes simplex virus 1 is an endoribonuclease with a substrate specificity similar to that of RNase A". J. Virol. 80 (18): 9341–5. doi:10.1128/JVI.01008-06. PMID 16940547.
- ↑ Skepper JN, Whiteley A, Browne H, Minson A (June 2001). "Herpes simplex virus nucleocapsids mature to progeny virions by an envelopment --> deenvelopment --> reenvelopment pathway". J. Virol. 75 (12): 5697–702. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.12.5697-5702.2001. PMID 11356979.
- ↑ Granzow H, Klupp BG, Fuchs W, Veits J, Osterrieder N, Mettenleiter TC (April 2001). "Egress of alphaherpesviruses: comparative ultrastructural study". J. Virol. 75 (8): 3675–84. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.8.3675-3684.2001. PMID 11264357.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Pinnoji RC, Bedadala GR, George B, Holland TC, Hill JM, Hsia SC (2007). "Repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor/neuronal restrictive silencer factor (REST/NRSF) can regulate HSV-1 immediate-early transcription via histone modification". Virol. J. 4: 56. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-4-56. PMID 17555596.
- ↑ Bedadala GR, Pinnoji RC, Hsia SC (2007). "Early growth response gene 1 (Egr-1) regulates HSV-1 ICP4 and ICP22 gene expression". Cell Res. 17 (6): 546–55. doi:10.1038/cr.2007.44. PMID 17502875.
- ↑ Roizman B, Gu H, Mandel G (2005). "The first 30 minutes in the life of a virus: unREST in the nucleus". Cell Cycle 4 (8): 1019–21. PMID 16082207.
- ↑ Vogler BK, Ernst E (October 1999). "Aloe vera: a systematic review of its clinical effectiveness". The British Journal of General Practice 49 (447): 823–8. PMID 10885091. PMC 1313538. http://openurl.ingenta.com/content/nlm?genre=article&issn=0960-1643&volume=49&issue=447&spage=823&aulast=Vogler.
- ↑ BioVex initiates Phase 1 Clinical Trial with its genital herpes vaccine, ImmunoVEXHSV2 http://www.biovex.com/03_04_10_Immunovex_trial.html
- ↑ Middleton PJ, Petric M, Kozak M, Rewcastle NB, McLachlan DR (May 1980). "Herpes-simplex viral genome and senile and presenile dementias of Alzheimer and Pick". Lancet 315 (8176): 1038. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(80)91490-7. PMID 6103379.
- ↑ Dobson CB, Itzhaki RF (1999). "Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer's disease". Neurobiol. Aging 20 (4): 457–65. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(99)00055-X. PMID 10604441.
- ↑ Pyles RB (November 2001). "The association of herpes simplex virus and Alzheimer's disease: a potential synthesis of genetic and environmental factors" (PDF). Herpes 8 (3): 64–8. PMID 11867022. http://www.ihmf.com/journal/download/83pyles(64)vol864.pdf.
- ↑ Itzhaki RF, Lin WR, Shang D, Wilcock GK, Faragher B, Jamieson GA (January 1997). "Herpes simplex virus type 1 in brain and risk of Alzheimer's disease". Lancet 349 (9047): 241–4. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)10149-5. PMID 9014911.
External links
- Mayo Clinic on Cold Sores
- Genital Herpes - Public Health Agency of Canada
- UK Genital Herpes Resource Site
- NHS Health Encyclopaedia - Information on Cold Sores
- American Social Health Association article on differences between HSV-1 and -2
- Cold sore virus secret revealed BBC News
- Recombinant herpesviruses used in gene therapy
- Herpes simplex: Host viral protein interactions: A database of HSV-1 interacting host proteins
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||